A car's braking system, much like a conductor leading an orchestra, plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth stops and safe journeys. Understanding its components and mechanisms is essential for all car owners. In this comprehensive beginner's guide, we will look into the crucial importance of the car braking system for overall safety. We will explore the common types of brakes, including drum and disc brakes, shedding light on their unique advantages and differences.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a good understanding of car braking systems, empowering you to make informed decisions and keep your brakes in top-notch condition. Let's dive in and demystify the world of car braking systems.
What is Brake System In Automobile?
The car braking system is a vital and sophisticated arrangement of various components working together to effectively slow down and stop the vehicle when required. It accomplishes this by converting the car's kinetic energy into heat energy, which is then dissipated to reduce the car's speed or bring it to a complete stop.
This system ensures safe driving by providing control over the vehicle's motion and preventing accidents. Understanding the intricacies of the car braking system empowers car owners to recognise potential issues, perform regular maintenance, and ensure the brakes function optimally, contributing to overall road safety.
How Does a Car Braking System Work?
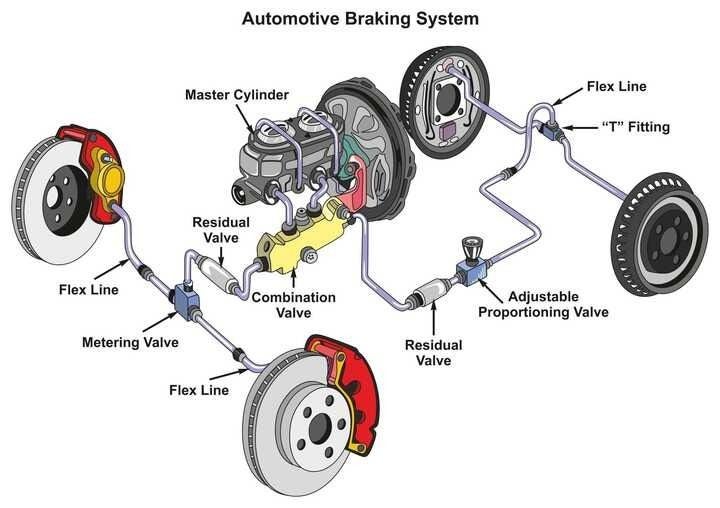
The car braking operates through a series of interconnected components, each playing a specific role in the braking process. Let's look into the details of how the car braking system works:
- Brake Pedal
- When you press the brake pedal with your foot, it initiates the braking process
- The brake pedal is connected to the master cylinder, which is the heart of the braking system
- Master Cylinder
- The master cylinder is a hydraulic device responsible for converting the mechanical force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure
- When you press the brake pedal, it pushes a piston inside the master cylinder, building up hydraulic pressure in the brake lines
- Brake Lines
- The hydraulic pressure generated by the master cylinder is transmitted through brake lines to the individual brake callipers or wheel cylinders at each wheel
- These brake lines are durable and made to withstand high pressures to ensure efficient braking
- Brake Calipers/Wheel Cylinders
- Depending on the type of brake system (disc or drum), your car will have either brake callipers or wheel cylinders
- These components act as actuators, converting hydraulic pressure back into mechanical force
- Brake callipers apply force to the brake pads, while wheel cylinders push the brake shoes against the drums
- Brake Pads/Shoes
- The final stage of the braking process involves the brake pads or shoes making contact with the brake rotors or drums
- These components are lined with a special friction material that creates the necessary friction to slow down or stop the car
- When the brake pads or shoes clamp down on the spinning rotors or drums, it creates resistance, converting the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle into heat energy, and thus, decelerating the car
Also Read : When Should I Replace My Car Brake Pads? – Here’s How to Know
Types of Car Brakes
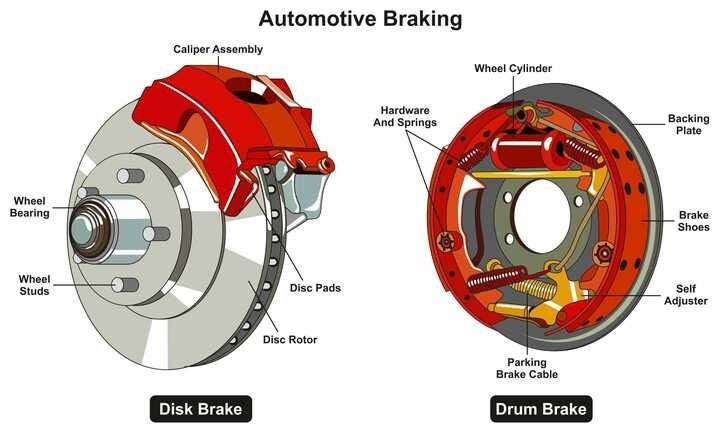
It is crucial to understand the different types of brakes in your car to make informed decisions about maintenance, replacement, or upgrades. While disc brakes are widely favoured for their performance, drum brakes still have their place in specific vehicle configurations.
Let's take a closer look at the different types of brakes in cars:
Drum Brakes
- Drum brakes are an older-style braking system commonly found in the rear wheels of some cars
- They consist of brake shoes, which are curved metal pads lined with friction material, and a drum, a round metal surface
- When you press the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure forces the brake shoes to expand against the inside of the drum, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle
- Drum brakes are cost-effective and simple in design, making them suitable for certain vehicles and driving conditions
- They can be less effective at dissipating heat compared to disc brakes, which can lead to reduced braking performance under prolonged heavy use
Disc Brakes
- Disc brakes are the most common braking system in modern cars
- They consist of brake pads, callipers, and a disc rotor attached to the wheel hub
- When you apply the brakes, hydraulic pressure forces the brake pads to squeeze against both sides of the disc rotor, generating friction and decelerating the vehicle
- Disc brakes offer superior performance, better heat dissipation, and enhanced stopping power compared to drum brakes
- They are also more responsive and provide consistent braking performance, particularly during heavy braking
- There are two types of disc brakes: floating calliper disc brakes and fixed calliper disc brakes
- Floating callipers slide on mounting pins, while fixed callipers are mounted rigidly in place
- Regular inspection and maintenance of disc brakes are essential to ensure their proper functioning and longevity
Carbon-Ceramic Brakes
- These high-performance braking systems are often used in sports cars and luxury vehicles
- They feature discs made from a composite of carbon fibre and ceramic materials
- The advantages of carbon-ceramic brakes include reduced weight, enhanced heat resistance, and increased longevity
- These brakes are ideal for high-performance applications
Drum vs. Disc Brakes
As we go deeper into the fascinating world of car braking systems, we need to take a closer look at the two primary types: Drum Brakes and Disc Brakes. Understanding their key differences and applications will empower us as car owners to make informed decisions about our vehicle's maintenance.
To aid in this comparison, we've organised a comprehensive table highlighting the distinct features of each braking system. Take a look:
| Aspect | Drum Brakes | Disc Brakes |
| Construction | Consist of a round drum and brake shoes | Comprise of a flat rotor and brake callipers |
| Friction Surface | Internal, enclosed within the drum | External, exposed for cooling |
| Heat Dissipation | Poor heat dissipation | Excellent heat dissipation |
| Performance | Generally less efficient | More efficient, better-stopping power |
| Fading | More prone to brake fade | Less prone to brake fade |
| Cooling | Less effective cooling | Effective cooling through ventilation |
| Weight | Typically lighter | Slightly heavier |
| Maintenance | Easier maintenance and lower cost | May require more frequent maintenance |
| Cost | Usually cheaper | Slightly more expensive |
| Applications | Commonly used in smaller and older vehicles | Widely used in modern cars |
| Performance in Rain | May perform slightly better in wet conditions | Perform well in wet conditions |
| Noise | Tend to be noisier during operation | Quieter operation |
| Space Requirements | Require more space due to internal components | Require less space due to compact design |
| Complexity | Simpler design and construction | More complex design and components |
Also Read : Things you should NOT do while driving an automatic car
How to Choose the Right Type of Brakes for a Car
The process of selecting the ideal brake system for a vehicle requires a meticulous examination of several critical factors. To make an informed decision, consider the following elements:
1. Vehicle Type
- The choice of brake system should align with the characteristics of the vehicle
- Smaller cars often feature a combination of disc brakes in the front and drum brakes in the rear
- Larger vehicles may employ disc brakes on all wheels to accommodate the increased demands
2. Driving Conditions
- The environment in which you typically drive should guide your brake system selection
- If you frequent hills or mountains, a robust braking system is essential to handle the added stress and heat generated during descents
3. Brake Pad Material
- Different brake pad materials cater to specific driving conditions
- Ceramic brake pads, for instance, are celebrated for their low noise and minimal dust production, making them suitable for urban driving
- In contrast, semi-metallic pads offer superior heat dissipation, ideal for high-performance applications or heavy loads
4. Maintenance Considerations
- Evaluate your willingness to engage in brake system maintenance
- Disc brakes are generally easier to inspect and maintain compared to drum brakes
Also Read: Signs That Your Brakes Are Unsafe
How to Maintain Your Car's Braking System
Maintaining your car's braking system is essential for your safety and the longevity of your vehicle. By following these maintenance tips and scheduling regular inspections, you can ensure that your brakes perform optimally, providing you with a smooth and secure driving experience on India's roads.
Here are some tips for the same:
Regular Inspections
- Schedule routine brake inspections with a qualified mechanic or at authorised service centres to detect any signs of wear, damage, or potential issues with the braking system
Brake Fluid Flush
- The brake fluid is a critical component of the hydraulic brake system, responsible for transmitting force from the brake pedal to the brakes
- Over time, brake fluid can absorb moisture, leading to reduced braking efficiency and potential damage to brake components
- It is essential to replace the brake fluid as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer, typically every two years or as specified in the owner's manual.
Brake Pad/Shoe Replacement
- The brake pads (in disc brakes) or brake shoes (in drum brakes) are crucial for creating the friction necessary to stop the vehicle
- As you use your brakes, the brake pads or shoes gradually wear down
- It is essential to monitor their thickness regularly and replace them when they reach the minimum recommended thickness, typically indicated by wear indicators on the pads or shoes
Rotor/Disc Resurfacing or Replacement
- The brake rotors (in disc brakes) are the flat, circular metal discs that the brake pads press against to stop the vehicle
- Over time, the rotors can develop uneven surfaces due to friction and heat
- If you experience vibrations or pulsations while braking, it might indicate warped rotors
- Depending on their condition, the rotors may need to be resurfaced (also known as machining) to restore a smooth, even surface
- In severe cases or if the rotors are too thin, replacement may be necessary for optimal braking performance
Brake System Bleeding
- Brake system bleeding is a maintenance procedure that involves removing air bubbles from the brake lines and callipers or wheel cylinders
- Air in the brake system can lead to a spongy brake pedal feel and reduced braking efficiency
- Bleeding the brakes is especially important after brake fluid replacement, brake component repairs, or if you notice a decrease in braking performance
- This process should be performed with precision and is often best left to experienced mechanics to ensure all air bubbles are effectively removed
The Bottom Line
A well-maintained car braking system is vital for road safety. Understanding how it works and the different types of brakes empowers informed decisions about maintenance. Regular inspections and timely replacements ensure reliable stopping power, keeping you safe on every journey. Take care of your brakes, and they'll take care of you. Stay safe on the road with a well-maintained braking system.
FAQs
Q. What are the signs of a failing braking system?
Signs of a failing braking system include squealing or grinding noises, vibrations while braking, longer stopping distances, and a spongy brake pedal. Any of these signs warrant immediate attention and inspection by a professional mechanic.
Q. How often should I have my brakes serviced?
Brake servicing frequency depends on driving conditions and usage. It's generally recommended to have brakes inspected at least once a year or every 12,000 miles, and more frequently if you notice any abnormal brake behaviour.
Q. What is the difference between disc brakes and drum brakes?
Disc brakes use callipers and rotors to apply braking force, offering better heat dissipation and braking performance, while drum brakes use brake shoes and a drum, suitable for lighter vehicles and rear wheels.
Q. What are anti-lock brakes?
Anti-lock brakes (ABS) are a safety feature that prevents wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing drivers to maintain control and steer the vehicle safely.
Q. What is an emergency brake?
The emergency brake, also known as the parking brake, is a manual braking system designed to hold the vehicle in place when parked. It's operated separately from the main braking system and can be useful in emergencies or when parking on steep inclines.














-(1).jpg&w=828&q=75)


.webp&w=828&q=75)
.jpg&w=828&q=75)






-(1).jpg&w=640&q=75)

.webp&w=640&q=75)
.jpg&w=640&q=75)









