Get behind the wheel of an electric car and you can feel the therapeutic rhythm of clean and dynamic energy coursing through your veins. The hum of the electric motor, the smooth acceleration, the instant torque—the way electric cars work, feels like magic. It's as if you're driving a machine that's come to life, a creature that's been awakened from a long slumber.
Electric vehicles, or EVs as they're often called, are a marvel of modern engineering. They represent the pinnacle of automotive technology, combining efficiency, sustainability, and sheer driving pleasure in a way that traditional petrol-powered cars simply can't match.
How do electric cars work, and what's the secret behind the electric vehicle technology and their environmental credentials? In this blog, we'll look into the working principle of electric vehicles, exploring everything from the definition of an EV to the nuances of how they function. So, let's plug in and get started on this electrifying and immersive journey to understand the working principle of electric vehicle technology.
How do Electric Cars Work?
Electric cars, or EVs, are powered by electric motors that draw their energy from a set of rechargeable batteries. These motors drive the wheels of the vehicle, just like in a traditional petrol or diesel powered car. However, the way that an electric car produces power is very different.
The batteries that power an electric car are made up of thousands of small cells, which are linked together in series to create a large battery pack. These battery packs are then mounted within the vehicle, typically beneath the floor or in the boot. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, an electronic signal is sent to the motor, which then draws power from the battery pack.
What are the Key Components of Electric Cars?
Electric cars rely on different components to function. From the battery and electric motor to the power electronics, each component plays a critical role in delivering the smooth, efficient, and environmentally friendly performance that electric cars are known for.
Let's take a look at these components in detail:
1. Battery
- Electric cars rely on high-capacity lithium-ion batteries for energy storage
- These batteries power the electric traction motor, and they are the main power source of the vehicle
2. Charging Port
- The charging port is where the car connects to external charging sources, including home chargers and public charging stations
3. DC/DC Converter
- The DC/DC converter converts high-voltage direct current (DC) from the main battery into lower-voltage DC needed for various systems
- In short, it is the power regulator that ensures efficient power distribution throughout the vehicle
4. Electric Traction Motor
- The electric traction motor is responsible for generating mechanical motion to drive the car's wheels
- It is like a propulsion engine that turns electrical energy from the battery into forward or reverse motion
5. Onboard Charger
- The onboard charger or the charging control unit manages the flow of electricity from external sources into the traction battery
- It allows the car to recharge efficiently when connected to a charging infrastructure
6. Power Electronics Controller
- Power electronics control, optimise, and manage the energy flow between the battery, motor, and other vehicle systems
- They ensure the vehicle operates efficiently and delivers performance
7. Thermal Systems
- Electric cars require optimal thermal management to regulate component temperatures
- Cooling systems prevent overheating, enhancing performance and longevity
8. Traction Battery Pack
- The traction battery pack houses the battery cells that store energy for the vehicle
- It's crucial for powering the electric motor and other car functions
9. Electric Transmission
- Electric cars commonly employ single-speed transmissions or direct-drive systems
- These systems efficiently transfer power from the motor to the wheels, eliminating the need for complex gear changes
Also Read: Hybrid Car VS Electric Car
How Does Charging Work for an Electric Vehicle?

Charging an electric car is a breeze once you know the ropes. It is essential to understand the charging process to ensure that your electric car is always ready to go when you need it.
Here's a breakdown of the charging process:
1. Plugging In
- Electric cars are charged by plugging them into an electric outlet
- You can charge at home using a standard electrical outlet or at a public charging station
- The time needed to fully charge depends on the charger type and battery size
2. Charging Connectors
- The Type 2 connector is the most common for AC charging in India
- Some public stations offer DC fast charging, which significantly reduces charging time
3. Home Charging
- Most electric cars come with a home charging cable for your convenience
- Home charging is slower but cost-effective, making it a sensible option to charge overnight or during off-peak hours to save on electricity costs
4. Planning Your Charges
- Plan your charging around your daily routine to ensure your car is ready when you need it
- Use public charging stations for quick top-ups during longer journeys
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Cars
What are the Different Types of Electric Cars?
Electric cars come in different shapes, sizes, and styles, and there are several different types to choose from, each with its unique characteristics and features.
Primarily, there are four different types of electric cars, and they are as follows:
1. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- BEVs are the most common type of electric car, and they are powered exclusively by an electric motor that is driven by a battery pack
- BEVs have no internal combustion engine and produce zero emissions, making them an excellent choice for environmentally conscious drivers
- They have a range of up to several hundred miles on a single charge, but recharging can take several hours.
2. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
- HEVs combine an electric motor with a conventional gasoline engine, and they use a battery pack to store energy
- HEVs can switch between the electric motor and gasoline engine depending on the driving conditions
- HEVs offer improved fuel economy and reduced emissions compared to conventional gasoline cars
3. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs)
- PHEVs are similar to HEVs, but they have a larger battery pack that can be recharged by plugging into an electric outlet
- PHEVs can operate in electric-only mode for short distances, but they can also switch to the gasoline engine when needed
4. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs)
- FCEVs use a fuel cell to generate electricity from hydrogen, which is then used to power an electric motor
- FCEVs are still relatively rare, but they offer the potential for zero-emissions driving without the need for a battery pack
Also Read: Pros and Cons of Electric Cars
EV Batteries and Their Capacity

Electric vehicles are becoming more and more popular as people start to realise the many benefits they offer, such as reduced emissions and lower running costs. At the heart of the EVs are batteries.
Let's take a closer look at the types and capacities of EV batteries:
1. Battery Types
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are popular for being lightweight, long-lasting, and cost-effective
- Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries are typically used in hybrid vehicles as they are durable but heavier
2. Understanding Capacity (kWh)
- Capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and indicates the amount of energy a battery can store
- Higher kWh means longer travel on a single charge
- For instance, a 40 kWh battery covers about 200-250 km, while a 100 kWh battery can manage up to 600 km
3. Charging Considerations
- Charging time varies with battery capacity, which means that a higher kWh battery takes longer to charge
- Faster charging requires more powerful stations, with public chargers offering 7-22 kWh and home chargers around 3-7 kWh
4. Range Factors
- Remember, battery capacity isn't the sole factor influencing range
- Driving style, weather, and vehicle weight also impact how far your EV can go on a single charge
- Thus, choosing the right battery capacity involves considering all these elements to match your needs
Also Read: Cheapest Electric Cars in India
How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Car?
One of the biggest concerns for many people when purchasing an electric car is how long it takes to charge. The answer to this question can vary depending on the type of charger being used, the size of the battery, and the range needed for the vehicle.
The time it takes to charge an electric car can range from just a few minutes to several hours or even overnight. The fastest charging option is using a DC fast charger, which can charge an electric car battery up to 80% in as little as 30 minutes. However, not all electric cars are equipped with DC fast charging capabilities.
Alternatively, a Level 2 charger, which can be installed at home or public charging stations, can charge an electric car in 4-8 hours depending on the size of the battery. A standard 120-volt outlet can also be used, but it can take significantly longer, usually up to 20 hours or more.
It's worth noting that electric car charging times can also vary depending on the temperature and weather conditions. Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can affect the charging time and the range of the vehicle. However, as technology continues to improve, charging times are expected to decrease, making electric cars even more convenient and accessible for everyone.
Here's a table to help you understand the average time it takes for some of the popular electric cars to charge from approximately 0-80% using the bigger, more powerful, faster DC chargers:
| Car | Body Type | Driving Range(km/charge) | Charging Time(0-80%) |
| Kia EV6 | Sedan | 708 | 18 minutes |
| Hyundai Ioniq 5 | SUV | 631 | 18 minutes |
| Tata Nexon EV Max | SUV | 453 | 56 minutes |
| BYD E6 | MPV | 521 | 50 minutes |
| BYD Atto 3 | SUV | 521 | 50 minutes |
| Hyundai Kona EV | SUV | 452 | 57 minutes |
| Tata Tiago EV | Hatchback | 315 | 60 minutes |
| Tata Tigor EV | Sedan | 315 | 60 minutes |
| MG ZS EV | SUV | 461 | 60 minutes |
Also Read: Upcoming Electric Cars Under 8 lakh in India
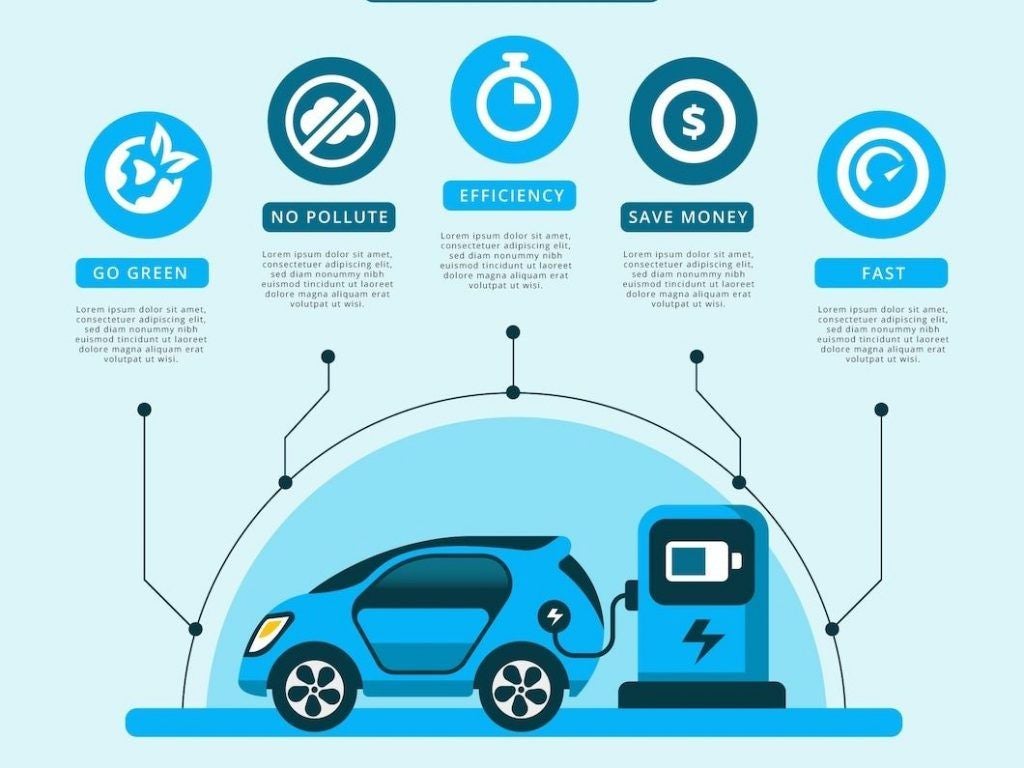
Benefits of Electric Cars
Electric cars are rapidly emerging as a promising alternative to traditional fuel-powered vehicles, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious consumers in India, promoting sustainability and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Here are some key benefits of electric cars:
- Electric cars produce zero to minimal tailpipe emissions, making them environmentally friendly and contributing to cleaner air quality.
- EVs are more energy-efficient and have fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance and operational costs.
- With electricity being more affordable than petrol and diesel, EV owners can enjoy significant savings on fuel.
- EVs run silently, contributing to reduced noise pollution in urban areas.
- Electric motors provide instant torque, leading to quick acceleration and an enjoyable driving experience.
- The Indian government offers various incentives and subsidies to promote the adoption of electric vehicles.
- EVs can be charged at home using a standard electrical outlet or at public charging stations, offering convenience and flexibility.
- While electric cars might have a higher upfront cost, long-term savings in fuel and maintenance can offset this expense.
- By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, electric cars play a part in mitigating climate change and environmental conservation.
Also Read: Best Electric Cars In India
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, electric cars are a fascinating blend of advanced technology and environmental consciousness. They are quickly becoming the future of transportation and are here to stay. With their silent motors, quick acceleration, and reduced carbon footprint, it's no wonder that they are gaining popularity among drivers worldwide.
As Elon Musk once said, "Electric cars are not only the future, but they are also the present." And he couldn't be more right. With more and more car manufacturers jumping on board with the electric trend, it's clear that the days of gasoline-fuelled cars are numbered. From the sleek and stylish Maruti Suzuki YY8 to the affordable and practical Citroen eC3, there's an electric car out there for everyone. If you're looking for an electric car that is as versatile as you are, make sure to check out our guide to the Upcoming Electric Cars in India Under 30 lakh
So, whether you're a die-hard petrolhead or a staunch environmentalist, there's no denying the appeal of electric cars. They're energy-efficient, cost-effective, and just plain cool. Who knows, maybe one day you'll be reminiscing about the days when you used to drive cars that ran on good old-fashioned petrol. In the meantime, let's enjoy the ride towards a brighter, cleaner, and electric future!
FAQs
Q. How do electric cars work?
Electric cars operate by converting stored electricity into motion through an electric motor, which is controlled by an onboard computer. They can also recharge the battery using regenerative braking.
Q. How long do electric car batteries last?
The lifespan of electric car batteries varies but generally lasts 8 to 10 years or up to 200,000 kilometres before needing replacement.
Q. Do electric cars need oil?
No, electric cars do not require oil changes like conventional cars do. Electric cars use a battery and electric motor to power the vehicle and do not have an internal combustion engine that requires lubrication.
Q. How much does a battery cost for an electric car?
Battery costs for electric cars range from ₹4 lakh to ₹11 lakh depending on the battery size, vehicle make, and model. Prices are expected to decrease with improved battery technology and production efficiency.
Q. Do electric cars have gears?
Electric cars use a single-speed transmission or direct drive system, eliminating the need for traditional gears found in gasoline-powered vehicles.










.jpg&w=828&q=75)










.jpg&w=828&q=75)




.webp&w=640&q=75)
-(1).webp&w=640&q=75)




