Welcome to our blog about power steering systems in cars! Ever wondered how effortlessly you can turn your car's steering wheel? It's all thanks to the power steering system. In this blog, we're going to break down what power steering is, its advantages, and how it works.
From traditional power steering in cars to the modern electric power steering system, we've got the basics covered. We'll also touch on the types of power steering systems and give you a glimpse into their inner workings. And, of course, we'll settle the debate between Power Steering vs. Manual Steering. Let's get started!
What is a Power Steering System?
Unlike the good old days, most modern cars require minimal effort to turn the wheel, thanks to a clever invention called power steering. It's a system designed to significantly reduce the physical effort needed to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds and during parking manoeuvres.
In short, power steering is a mechanism that makes driving more comfortable and less tiring, even during long journeys or while navigating tight spaces.
How Does the Power Steering System Work?
Most modern cars come equipped with power steering. But how does this magic happen? Let's take a closer look at power steering and understand the role of each of its components:
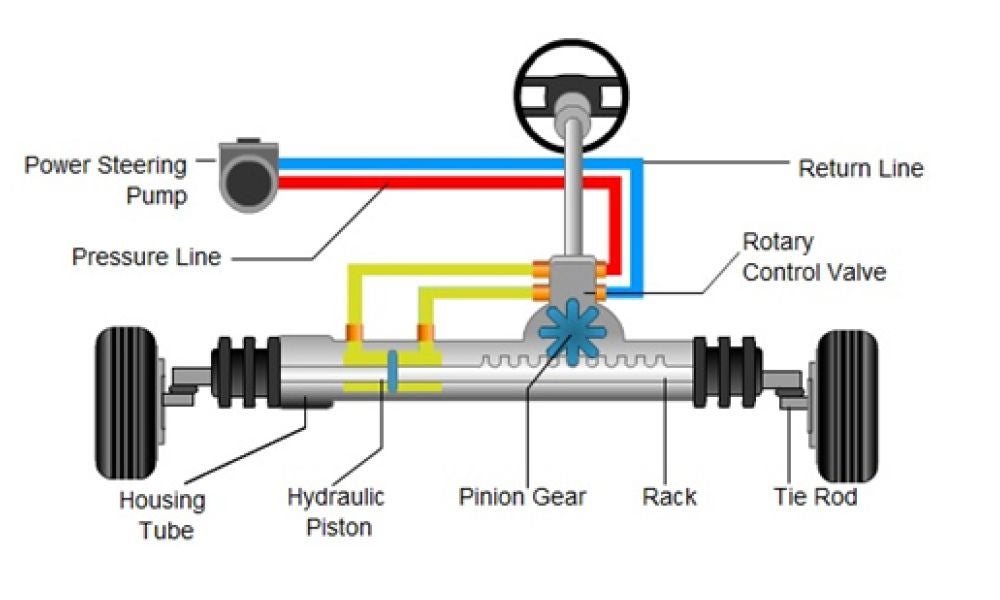
Traditional Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
Engine
- The system utilises the engine's power transmitted through a drive belt
- This belt connects the engine's crankshaft to the hydraulic pump
Hydraulic Pump
- This pump is the workhorse of the system and converts the engine's rotational motion into high-pressure hydraulic fluid
- It's typically a vane pump with rotating blades inside a chamber that traps fluid and forces it out at high pressure as the shaft rotates
Steering Wheel
- As you turn the wheel, it rotates a shaft connected to the steering gear
Steering Gear
- This component translates the rotational motion of the steering wheel shaft into a linear movement
- It can be a rack and pinion system where the shaft rotates a pinion that meshes with a rack
- The rack then moves left or right, depending on the direction you turn the wheel
Control Unit (Valve)
- Connected to the steering gear shaft is a control valve which acts as a directional control based on the driver's input
- It consists of a spool that moves based on the rotation of the shaft, directing the high-pressure fluid from the pump to the hydraulic cylinder
Hydraulic Cylinder
- This cylinder houses a piston connected to the car's steering linkage through a tie rod
- The cylinder has two chambers, one on each side of the piston
High-Pressure Fluid
- Depending on the direction you turn the wheel, the control valve directs the high-pressure fluid to one side of the cylinder while the other side remains open to a reservoir
Piston
- The force of the pressurised fluid pushing against the piston in one chamber creates a torque that assists in turning the car's wheels in the desired direction
- This significantly reduces the effort required on the steering wheel
Centering Spring
- This spring helps the wheels return to the centre position once you straighten the steering wheel
Reservoir
- This tank stores the hydraulic fluid and allows for expansion and contraction due to temperature changes
Also Read : Best Suspension Cars in India
Modern Electric Power Steering (EPS)
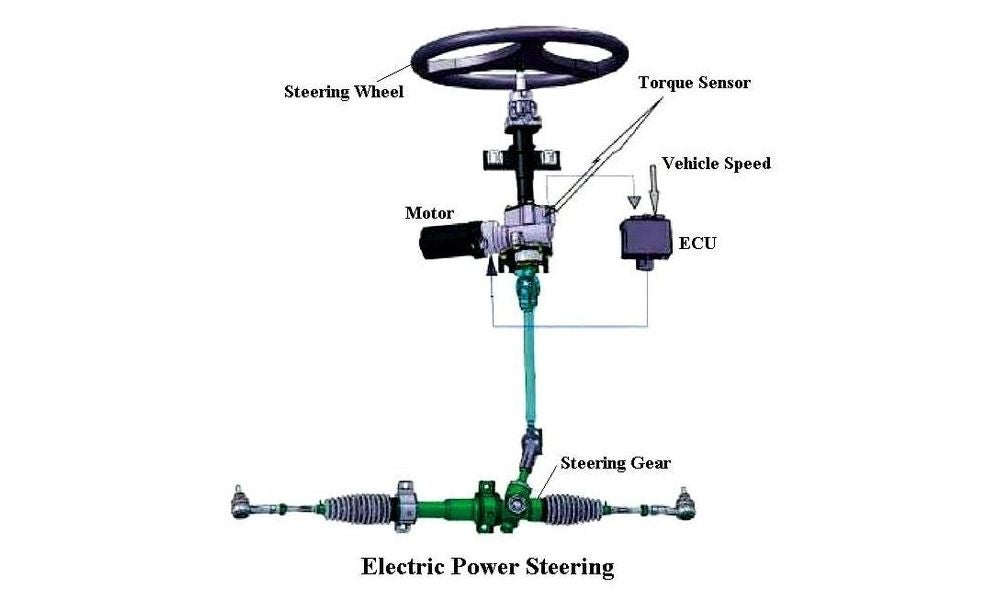

While the basic principle remains the same (reducing steering effort), EPS replaces the hydraulic components with an electronic system:
Torque Sensor
- This sensor, located in the steering column, detects the direction and amount of force you apply to the steering wheel
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
- This unit is the brain of the system and receives signals from the torque sensor, speed sensors, and other car systems to determine the appropriate level of assistance
Electric Motor
- Based on the information received, the ECU controls an electric motor mounted on the steering gear or column
- This motor assists the steering system, making it easier to turn the wheels
Types of Power Steering System
Now that you know the components and the basic functioning of the power steering system, let's take a look at its types.
Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
- This is the most traditional form of power steering, found in a wide range of vehicles, from older cars to heavy-duty trucks
- It uses a belt-driven hydraulic pump, powered by the engine, to pressurise hydraulic fluid
- This fluid is directed by a control valve based on the driver's steering input
- A hydraulic cylinder attached to the steering system receives the fluid pressure, creating the force that assists in turning the wheels
Advantages of Hydraulic Power Steering
- Proven and reliable technology
- Provides a good feel of the road
Disadvantages of Hydraulic Power Steering
- Constant use of a belt-driven pump reduces engine efficiency
- Prone to fluid leaks over time and can require more maintenance
Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS)
- This system combines elements of both hydraulic and electric power steering
- It uses hydraulic boost like a traditional HPS system but replaces the engine-driven pump with an electric pump
- Sensors monitor steering input, sending signals to an electronic control unit (ECU)
- The ECU activates the electric pump, generating the necessary hydraulic pressure to assist the driver
Advantages of Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering
- More fuel-efficient than HPS, as the pump only runs on demand
- Offers the robust feel of hydraulic steering
Disadvantages of Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering
- Still susceptible to the potential weaknesses of hydraulic systems like leaks
- More complex than pure HPS
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
- This is the most common type in modern vehicles and relies solely on electrical components, eliminating the need for hydraulics
- A torque sensor on the steering column detects the driver's input and sends a signal to an electronic control unit (ECU)
- The ECU calculates the required assist and activates an electric motor
- The motor provides steering assistance either by applying torque directly to the steering column or by applying torque to the rack-and-pinion gear
Advantages of Electric Power Steering
- Most fuel-efficient option, no engine power required
- Extremely reliable, with fewer moving parts to fail
- Offers flexibility in tuning the steering feel for different driving preferences
- Well-suited for integration with advanced driver-assistance systems
Disadvantages of Electric Power Steering
- Less 'natural' steering feel in some earlier implementations, though modern EPS systems are far better
Also Read : Tips on How to Keep Car Cool in Summer
Advantages of Power Steering System
Power steering systems significantly reduce the physical effort required to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds and during parking manoeuvres. This benefit is particularly valuable for drivers navigating congested urban areas or manoeuvring large vehicles.
Additionally, power steering enhances handling by providing more precise and controlled steering. While it reduces the "road feel" compared to non-powered systems, this translates to smoother steering inputs, less driver fatigue, and potentially faster reaction times in critical situations.
Power steering also contributes to a more comfortable driving experience by minimising muscle strain and fatigue, allowing drivers to focus more on the road and surrounding conditions. Furthermore, reduced fatigue can indirectly lead to improved safety by keeping drivers more alert and potentially aiding in avoiding collisions.
Functions of a Power Steering System
Traditional Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
- HPS systems significantly multiply the force applied by the driver to the steering wheel, making it easier to manoeuvre the vehicle
- These systems offer graduated levels of assistance based on driving conditions
- At higher speeds, where less turning effort is needed, the system provides less assistance for a more natural feel
- Conversely, at lower speeds, such as during parking or tight turns, HPS provides increased assistance for easier manoeuvring
- While HPS reduces physical effort, some systems incorporate a feedback mechanism that simulates some degree of road feel, providing drivers with a sense of connection to the road
Modern Electric Power Steering (EPS)
- While the core function of reducing steering effort remains the same, EPS performs this task differently
- EPS systems continuously monitor the direction and amount of force applied to the steering wheel through a torque sensor
- The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) analyses the driver's input and various car parameters like vehicle speed and road conditions
- Based on the analysed data, the ECU controls an electric motor to deliver the exact amount of assistance needed to turn the wheels in the desired direction
Also Read : 20 Car Dashboard Signs and Names
Difference Between Manual Steering and Power Steering
| Parameter | Manual Steering | Power Steering |
| Effort Required | Requires significant driver effort to turn the wheel, especially at slow speeds and when parking | Requires less driver effort to turn the wheel due to power assistance |
| Operating Principle | Driver's physical force directly translates to turning the wheels through mechanical linkages | A power source (electric or hydraulic) assists the driver's input to turn the wheels |
| Feedback | Driver feels a direct connection to the road and can sense changes in grip and surface conditions | Driver may experience less road feel due to power assistance |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally more fuel-efficient as there's no additional power source required for steering | May have slightly lower fuel efficiency due to the power source used for assistance |
| Cost | Generally less expensive due to simpler design | Generally more expensive due to additional components and technology |
| Maintenance | Generally lower maintenance costs due to fewer components | May have higher maintenance costs due to additional components and the potential for power system issues |
| Suitability | Suitable for experienced drivers who prefer a more engaging driving experience | Suitable for drivers of all experience levels who appreciate easier manoeuvring and reduced effort, especially in urban environments or while parking |
Difference Between Power Steering and Electric Steering
| Parameter | Power Steering | Electric Power Steering (EPS) |
| Power Source | Uses hydraulic fluid and a pump powered by the engine | Uses the car's electrical system and an electric motor |
| Components | Includes a pump, hoses, reservoir, steering gear, and rack | Includes an electric motor, torque sensor, control unit, and steering gear |
| Complexity | More complex with more moving parts | Simpler design with fewer moving parts |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance to check fluid levels and for potential leaks | Generally lower maintenance needs, as there is no fluid to change |
| Fuel Efficiency | Can slightly decrease fuel efficiency due to the engine powering the pump | Generally improves fuel efficiency, as the motor only uses power when steering |
| Performance | May offer better feedback and feel at higher speeds | May feel lighter and less responsive at higher speeds |
| Cost | Generally more expensive to buy and maintain | Generally less expensive to buy and maintain |
| Reliability | More prone to malfunctions due to hydraulic components | Generally more reliable due to fewer moving parts |
| Noise | May generate some pump noise at low speeds | Generally quieter as there are no hydraulic components |
Difference Between Electric Power Steering and Hydraulic Power Steering
| Parameter | Electric Power Steering (EPS) | Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS) |
| Power Source | Uses an electric motor powered by the car's battery | Uses a hydraulic pump driven by the engine's crankshaft |
| Fuel Efficiency | More fuel-efficient, as it only uses power when steering, not constantly like HPS | Less fuel-efficient, as the pump runs continuously, even when not steering |
| Maintenance | Generally requires less maintenance, with fewer components to wear out | Requires regular fluid changes and maintenance of the pump and system components |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to the more complex electronic components | Generally less expensive due to simpler mechanical design |
| Feel | Can feel less connected to the road due to the electronic assistance | Can offer a more direct and "connected" feel to the road |
| Environmental Impact | More environmentally friendly, as it consumes less energy and doesn't use hydraulic fluid | Less environmentally friendly due to the use of hydraulic fluid and its potential leaks |
| Reliability | Generally considered more reliable due to fewer moving parts and less prone to leaks | Can be less reliable due to potential leaks and wear on mechanical components |
| Compatibility | Well-suited for modern cars with advanced driver-assistance features | Less suitable for modern cars with advanced driver-assistance features that rely on precise steering control |
Best Cars with Power Steering System
Since most of the cars in the market come equipped with power steering, it is difficult to compile a list of the best cars with this feature. However, here are some of the most popular cars that have a power steering:
- Tata Punch
- Maruti Swift
- Tata Harrier
- Maruti Brezza
- Hyundai Creta
- Hyundai Verna
- Mahindra Thar
- Skoda Kushaq
- Mahindra Scorpio
- Mahindra XUV 700
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, the power steering system is the unsung hero behind the effortless turns of your car's steering wheel. Whether it's the traditional hydraulic power steering (HPS) or the modern electric power steering (EPS), these systems work in harmony to make your driving experience smoother and less fatiguing.
The advantages of power steering are clear – reduced effort, enhanced control, and a more comfortable ride. So, the next time you effortlessly navigate your car, remember, that it's the power steering system silently working its magic. Happy driving!
FAQs
Q. What is the power steering system?
The power steering system is a mechanism in cars designed to reduce the physical effort needed to turn the steering wheel. It uses hydraulic or electric assistance to make steering more manageable, especially at low speeds and during parking manoeuvres.
Q. What are the five functions of a steering system?
The steering system functions to multiply the force applied by the driver, providing graduated assistance based on driving conditions. It enhances handling, reduces driver fatigue, and contributes to a more comfortable driving experience. Additionally, power steering systems aid in returning the wheels to the centre position and maintain a connection to the road.
Q. Are there any disadvantages of power steering?
While power steering greatly improves driving comfort, it does have some disadvantages. Traditional hydraulic power steering systems may reduce engine efficiency due to the constant use of a belt-driven pump and are prone to fluid leaks over time, requiring maintenance. Electric power steering systems, while more fuel-efficient, may offer a less "natural" steering feel in some cases.
Q. Can I drive without power steering?
Yes, you can drive without power steering, but it requires more physical effort, especially at slow speeds or during parking. Cars with manual steering systems lack power assistance, making the steering wheel harder to turn compared to vehicles equipped with power steering.






.jpg&w=828&q=75)






.jpg&w=828&q=75)
.jpg&w=828&q=75)
.jpg&w=828&q=75)
.jpg&w=828&q=75)

.jpg&w=384&q=75)

.jpg&w=384&q=75)
.jpg&w=384&q=75)

.jpg&w=384&q=75)
.jpg&w=384&q=75)

.webp&w=384&q=75)








