Self-Driving Cars Explained: A Practical Guide

Updated on: 23rd April, 2024 IST

Revolutionary technology has the power to captivate or perplex us until we unravel its secrets. Enter self-driving, or autonomous cars—the epitome of cutting-edge innovation. These vehicles are equipped with state-of-the-art artificial intelligence (AI) systems that enable them to navigate roads and make human-like decisions without human intervention.
Beyond personal transportation, the future of AI extends to emergency services like ambulances and police operations. By leveraging AI-powered systems, emergency vehicles can navigate through traffic more efficiently, reducing response times and potentially saving lives.
In this guide to self-driving cars, we will look into the intricacies of this groundbreaking technology, explore its current limitations in India, and examine the profound impact AI can have on the world around us. So buckle up and get ready for an exhilarating journey into the future—or should we say the present?

Table of Contents
- The First Self-Driving Cars in the World
- Tesla's Autopilot
- How Do Self-Driving Cars Work?
- What Are the Different Levels of Self-Driving Cars?
- Level 5 — Full Automation
- Which Are the Key Players In The Market When It Comes to Self-Driving Cars?
- Advantages of Self-Driving Cars
- Disadvantages of Self-Driving Cars
- What Safety Features Do Self-Driving Cars Have?
- Differences Between Self-driving Cars and Regular Cars
- Can Self-Driving Cars Operate on Indian Roads?
- The Bottom Line
- FAQs
The First Self-Driving Cars in the World
The inception of self-driving cars can be traced back to the pioneering efforts of several companies and institutions. These achievements have laid the foundation for the advancements we witness today in the realm of self-driving cars.
Here are some key milestones in the development of self-driving technology:
Carnegie Mellon University
In the 1980s, Carnegie Mellon University's Navlab Project introduced the world's first fully autonomous vehicle, named "Navlab 1." This converted van successfully navigated a 100-mile journey using an array of sensors and computer systems.
Google's Waymo
Google's self-driving car project, now known as Waymo, emerged in 2009. Waymo's autonomous vehicles have logged thousands of kilometres on public roads, refining their technology and paving the way for future advancements.
Tesla's Autopilot
Tesla introduced its Autopilot feature in 2014. While not fully self-driving, it marked a significant step towards autonomous driving by combining adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and other features.
Autonomous Taxis in Singapore
In 2016, Singapore became the first city to launch a self-driving taxi service. The initiative, led by startup nuTonomy, allowed selected users to use autonomous taxis within a designated area, marking a significant milestone in the deployment of self-driving technology.
How Do Self-Driving Cars Work?
Self-driving cars operate through a combination of advanced sensors, intricate algorithms, and artificial intelligence (AI) systems. Here's a breakdown of the key components and processes involved in their functioning:
Sensors
Self-driving cars are equipped with an array of sensors that provide a comprehensive view of their surroundings. These sensors include radar, lidar (light detection and ranging), cameras, and ultrasonic sensors. They work together to detect and interpret objects, road markings, and other vehicles in real time.
Mapping and Localisation
High-definition maps are crucial for self-driving cars. These maps contain detailed information about the road network, traffic signs, speed limits, and more. Simultaneously, the vehicle uses GPS, sensors, and advanced algorithms to precisely determine its location on the map.
Perception and Decision-Making
Self-driving cars analyse the environment using sensors and make decisions in real-time. Advanced algorithms process the sensor data to identify objects, predict their behaviour, and calculate the best course of action. These decisions include controlling the acceleration, braking, and steering of the vehicle.
Control Systems
Self-driving cars employ sophisticated control systems to execute their decisions. These systems translate the calculated actions into the physical movements of the vehicle, precisely controlling its speed, direction, and braking.
Machine Learning
Self-driving cars also use machine learning techniques to continuously improve their performance. By analysing vast amounts of data collected during driving, AI systems can adapt and enhance their decision-making capabilities over time.

What Are the Different Levels of Self-Driving Cars?
The journey towards fully autonomous vehicles is categorised into six levels of automation, established by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). These levels define the extent to which a vehicle can operate without human intervention. Let's explore each level in detail:
Level 0 — No Automation
At Level 0, the vehicle operates with no autonomous capabilities, and the driver has full control and responsibility for all aspects of driving. This level represents traditional vehicles that lack any automated features.
Level 1 — Driver Assistance
Level 1 introduces basic driver assistance features, such as adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping assist. These systems can control certain aspects of driving, but the driver remains fully responsible for operating the vehicle and monitoring the road.
Level 2 — Partial Automation
Level 2 marks a significant advancement with systems that can simultaneously control two or more functions, like steering and acceleration. Examples include Tesla's Autopilot and General Motors' Super Cruise. However, the driver must remain attentive and ready to take control at any moment.
Level 3 — Conditional Automation
At Level 3, vehicles can handle most driving tasks under specific conditions and environments. The driver can relinquish control. However, the driver must be prepared to intervene if the system requests assistance. Level 3 systems are not yet widely available, and their regulatory approval remains a challenge.
Level 4 — High Automation
Level 4 vehicles are capable of performing all driving tasks within specific operational domains. They can operate autonomously in certain geographic areas or predefined routes without driver intervention. However, Level 4 vehicles may still allow the driver to take control if desired or necessary.
Level 5 — Full Automation
Level 5 represents the pinnacle of self-driving technology. Vehicles at this level can handle all driving tasks under all conditions. They require no human intervention and can navigate any road or environment that a human driver can. Level 5 vehicles are fully autonomous and don't even include traditional controls like steering wheels or pedals.
It's important to note that while Level 5 is the ultimate goal, current self-driving technologies available to consumers are primarily at Levels 1 and 2. Higher levels of automation are still undergoing development, testing, and regulatory scrutiny.
Which Are the Key Players In The Market When It Comes to Self-Driving Cars?
The development and adoption of self-driving cars have attracted numerous companies, ranging from automotive giants to technology firms. Here are some key players in the self-driving car market:
Waymo (Alphabet Inc.)
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google's parent company), is widely regarded as a leader in self-driving technology. With extensive testing and deployment, Waymo's autonomous vehicles have accumulated thousands of kilometres on public roads, showcasing their advanced capabilities.
Tesla
Tesla, through its Autopilot feature, offers advanced driver-assistance systems and continues to develop towards higher levels of automation. Tesla's vast fleet and data collection contribute to the continuous improvement of its self-driving capabilities.
Cruise (General Motors)
Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors, is dedicated to developing self-driving technology. Backed by substantial investments, Cruise aims to deploy a fleet of fully autonomous electric vehicles. They have conducted extensive testing in challenging urban environments like San Francisco, showcasing their commitment to safety and innovation.
Mobileye (Intel Corporation)
Mobileye, an Intel Corporation subsidiary, specialises in advanced driver-assistance systems and autonomous vehicle technologies. Their camera-based vision systems and computer vision algorithms play a crucial role in enabling self-driving features in various vehicles.
NVIDIA
NVIDIA, a prominent technology company, provides essential hardware and software solutions for autonomous vehicles. Their powerful AI platforms, such as the NVIDIA DRIVE platform, are used by numerous automakers and tech companies for developing self-driving technologies.
It's worth mentioning that traditional automotive manufacturers like BMW, Audi, Ford, and Toyota are also actively investing in self-driving research and development, collaborating with technology partners to stay competitive in this rapidly evolving market.
Advantages of Self-Driving Cars
Self-driving cars come equipped with a host of features that make them a lucrative option. Here are some of the key advantages of self-driving cars:
Improved Safety
According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), it is estimated that self-driving cars could potentially reduce road accidents by up to 94%. With advanced sensors, real-time data analysis, and quick response capabilities, autonomous vehicles can help prevent collisions and make roads safer for everyone.
Increased Efficiency
Through interconnected communication systems, autonomous vehicles can coordinate with each other, enabling smoother lane changes, reduced traffic jams, and improved overall traffic management. This efficiency also translates into time and fuel savings for commuters.
Enhanced Accessibility
With autonomous vehicles, individuals with limited mobility can gain greater independence and access to transportation options that were previously challenging or unavailable.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Autonomous vehicles can be programmed to drive more efficiently, optimising routes and minimising fuel consumption. Additionally, the rise of autonomous electric vehicles would further reduce greenhouse gas emissions, helping combat climate change and improve air quality.
Increased Productivity and Comfort
With self-driving cars, commuting time can be transformed into productive time. Passengers can engage in work, relax, or pursue leisure activities during their journeys.
Disadvantages of Self-Driving Cars
The fact that autonomous vehicles are not yet accessible and affordable to the masses points to some of their drawbacks. Here are some of the key disadvantages of self-driving cars that need prompt remedial action:
Technological Limitations
Despite significant advancements, self-driving technology still faces challenges. Adverse weather conditions, complex traffic scenarios, and detecting certain objects (like pedestrians or cyclists) remain areas that require further development.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Implementing self-driving cars requires establishing comprehensive legal and regulatory frameworks to address liability, insurance, privacy, and cybersecurity concerns. Creating consistent regulations across regions and countries poses a significant challenge for widespread adoption.
Cost of Implementation
Currently, self-driving technology is expensive. The sensors, cameras, and computing systems required for autonomous driving come at a significant cost.
Job Displacement
The widespread adoption of self-driving cars may result in job displacement for individuals employed in the transportation sector, such as truck drivers or taxi drivers.
Ethical and Moral Considerations
Self-driving cars raise complex ethical dilemmas. For example, in critical situations where accidents are unavoidable, the autonomous system may have to make split-second decisions that involve choosing between different outcomes, potentially impacting the safety of passengers, pedestrians, or other vehicles.
What Safety Features Do Self-Driving Cars Have?
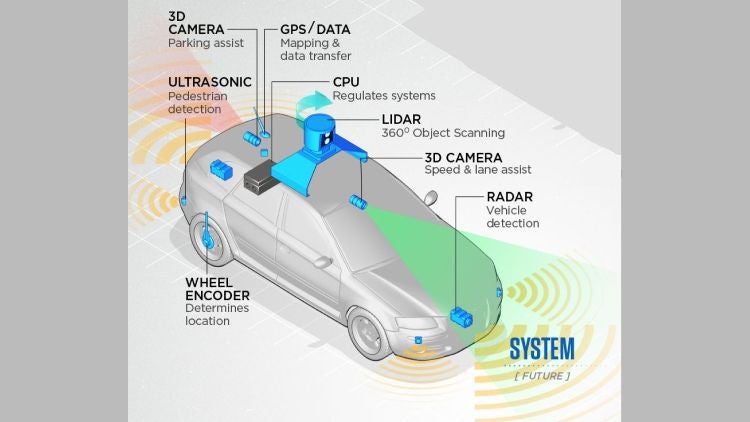
Self-driving cars are equipped with a range of impressive safety features designed to enhance the driving experience and prioritise passenger safety. Let's explore some of these features:
Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication (V2V)
This software enables self-driving cars to communicate with other vehicles, exchanging crucial data such as speed, position, distance, and traffic conditions. Through wireless connectivity, the vehicle becomes fully aware of its surroundings, enhancing safety and facilitating smoother driving.
Vehicle Guidance System
The vehicle guidance system incorporates advanced self-steering technology, allowing autonomous vehicles to navigate without human intervention. By combining motion strategy algorithms with path generators, self-driving cars can operate seamlessly and make informed decisions on the road.
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) System
Similar to Google Lens for self-driving cars, the AEB system enables vehicles to scan objects in their path and automatically apply brakes when necessary. This swift response helps prevent last-minute collisions, enhancing overall safety.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Powered by artificial intelligence (AI), ACC is a crucial component of self-driving car systems. This intelligent software adapts standard cruise control to account for obstacles and real-time traffic movement. It adjusts the vehicle's speed and position, ensuring a safe and efficient driving experience.
Blind Spot Detection
Spearheaded by Volvo, the blind spot detection system offers a comprehensive 360-degree assessment of surrounding traffic. By alerting drivers to potential blind spots, this technology significantly enhances safety and minimises the risk of accidents.
Reverse Parking Assist
Autonomous vehicles come equipped with a video monitoring system, utilising high-resolution cameras to autonomously park the vehicle. This feature provides convenience and precision, eliminating parking woes.
Lane-Keeping Assist (LKA)
The Lane-Keeping Assist technology plays a crucial role in maintaining vehicle alignment within designated lanes. By automatically adjusting the front wheels, this feature helps prevent unintentional drifting, promoting safer driving.
Differences Between Self-driving Cars and Regular Cars
While self-driving cars offer promising benefits, they are still in the early stages of development and deployment, and the transition to fully autonomous vehicles will require careful consideration of various factors. Here are the key differences between self-driving cars and regular cars:
Automation Level
Self-driving cars have varying levels of automation, whereas regular cars rely entirely on human drivers for control and operation.
Sensory Systems
Self-driving cars are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and LiDAR technology to perceive their surroundings, while regular cars rely on human senses and limited mirror views.
Decision-Making
Self-driving cars use artificial intelligence algorithms and complex software to make real-time decisions based on sensor inputs and data analysis, whereas regular cars depend on human judgement and experience.
Safety Features
Self-driving cars often feature advanced safety systems, such as collision avoidance, emergency braking, and pedestrian detection, which are not as prevalent in regular cars.
Can Self-Driving Cars Operate on Indian Roads?
Although self-driving cars are making remarkable strides globally, their presence is not yet felt in countries like India. The Indian driving landscape poses unique challenges which necessitate further adaptations and infrastructure improvements to accommodate autonomous vehicles effectively.
Self-driving cars have the potential to operate on Indian roads, but several challenges need to be addressed:
Road Conditions
Indian roads can be unpredictable, with potholes, uneven surfaces, and erratic traffic patterns, which pose challenges for self-driving cars.
Infrastructure
The lack of advanced infrastructure, including road markings, signage, and reliable GPS coverage, can impact the accuracy of self-driving car navigation systems.
Pedestrian Awareness
India has a high population density, and pedestrians often disregard traffic rules, making it challenging for self-driving cars to accurately detect and respond to their presence.
Public Acceptance
Widespread acceptance and trust in self-driving technology among the Indian public may take time to develop due to concerns about safety and job displacement.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, the future of self-driving cars is driven by continuous innovation and technological advancements. The recent introduction of India's first AI-powered car, the MG Astor, with its impressive array of Autonomous Level 2 features, exemplifies the progress being made in this field. With car manufacturers like Tesla and technology giants like Accenture already working on fully autonomous vehicles, it is clear that the dream of self-driving cars will soon become a reality.
As we eagerly await the arrival of fully autonomous cars, it's undeniable that the automotive industry is on the brink of a major transformation. The future promises exciting possibilities, and we can't help but be thrilled about what lies ahead. We are excited aplenty. You?
FAQs
Q. What guides a self-driving car?
A self-driving car is guided by a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI). The sensors collect data about the car's surroundings, and the AI uses this data to make decisions about how to drive the car.
Q. What three things do self-driving cars use to see?
Self-driving cars use cameras, radar, and lidar to be able to see objects such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic signs.
Q. Which self-driving car is the best?
The best self-driving car depends on the safety features and automation levels that are available. Currently, Tesla is known to manufacture some of the best electric cars with autonomous capabilities.
Q. Which is India's first car with AI technology?
The MG Gloster was the first car in India with Level 1 ADAS, which includes features such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and forward collision warning, among others.
Buy recently added cars
Other Blogs
- Recent
- Featured
Popular Cities to Sell Car


























